What is EMR?
An EMR Cluster
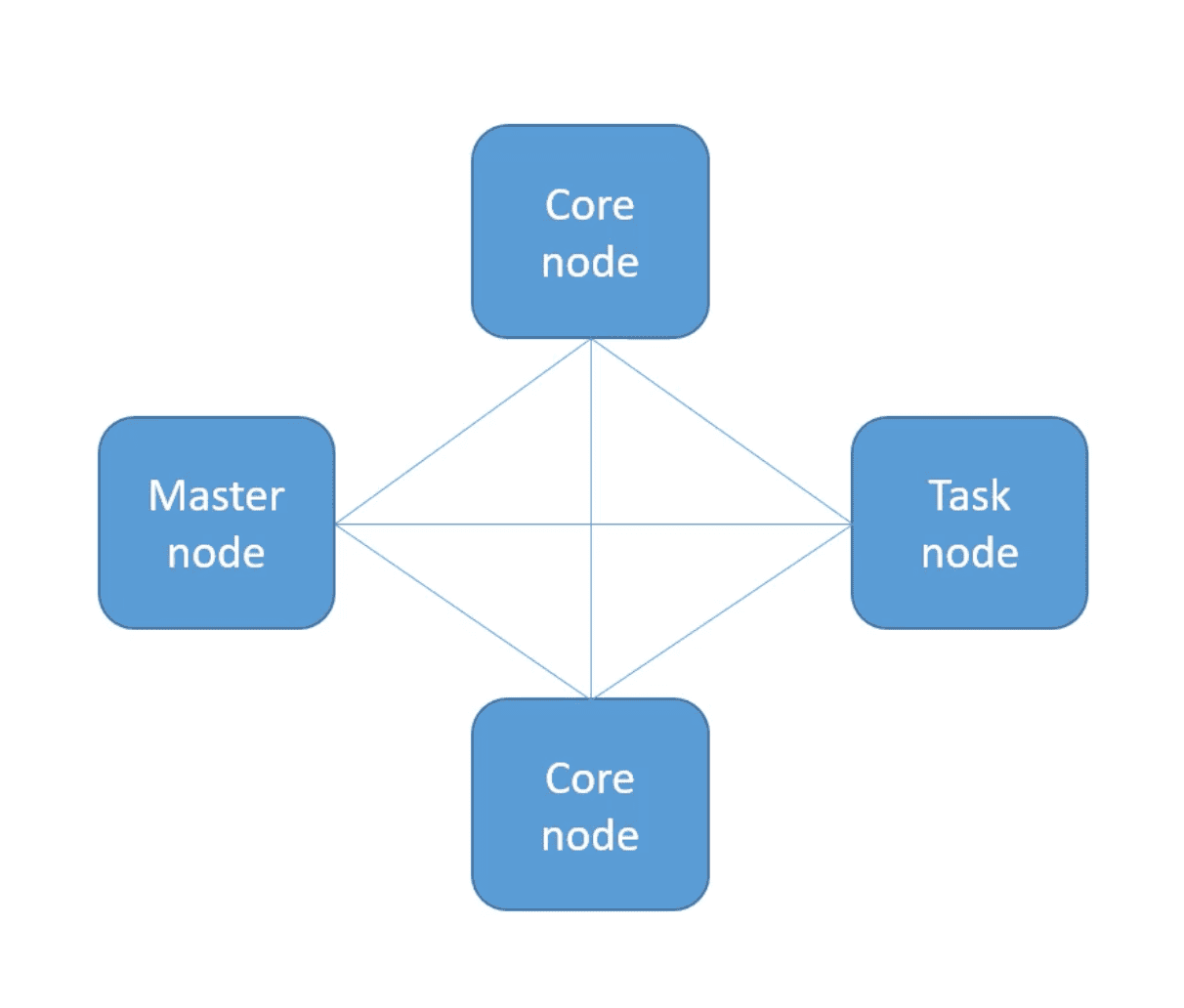
An EMR cluster is a group of EC2 Instances, where each instance is called a Node
Each node has a node type
- Master/Leader Node - Manages the cluster and distributes data and task to the nodes, an EMR cluster can have a single Node
- A cluster can have only one node, the same node acts as all node types
Core Node
- Hosts HDFS that store data in your cluster
- Scaling up down comes with its risks as data needs to replicated and made sure its okay to remove nodes
Task Node
- used to run tasks (compute + memory)
- can be scaled up and down
- A good use for spot instances
EMR and AWS Integration
- EC2: Provides the underlying instances for the nodes.
- VPC: Places the cluster within a virtual network.
- S3: Used to store input and output data (alternative to HDFS).
- CloudWatch: Monitors cluster performance and configures alarms.
- IAM: Configures permissions.
- CloudTrail: Creates audit trails for service requests.
- AWS Data Pipeline: Schedules and starts clusters for predefined steps.
EMR Storage
- HDFS (Hadoop Distributed File System):
- The default storage solution.
- Distributes data blocks (default 128MB) across the cluster with redundancy.
- Pros: Very fast performance because processing occurs locally where data is stored.
- Cons: Ephemeral; data is lost when the cluster terminates.
- EBS: Can be used to back HDFS.
- EMRFS:
- Solves the data persistence issue (data remains after cluster termination).
- Can use DynamoDB to track consistency.
- Local File System: Non-distributed, ephemeral storage