Architecture

Essentially a dedicated private connection between on-prem and aws in the high level. Core Components:
- Customer Router: Your on-prem router that connects to Direct Connect via a dedicated line.
- Direct Connect Location: AWS’s colocation facility where AWS provides a Direct Connect router (partner or AWS-managed).
- Cross Connect: Physical fiber link between your router and AWS’s router in the colocation.
- AWS Router (DX Router): Terminates the Direct Connect connection; connects to AWS backbone.
- Virtual Interfaces (VIFs):
- Private VIF: To access VPC resources.
- Public VIF: To access AWS public services (e.g., S3, DynamoDB).
- Transit VIF: For multiple VPCs via a Transit Gateway.
Data Flow:
On-prem → Customer Router → Cross Connect → AWS DX Router → VIF → VGW/Transit GW → VPC
and More
- Direct Connect Connection
- BGP
- LOA-CFA
- Direct Connect Gateway (DXGW)
- Transit Gateway
- Redundant Connections (for HA)
- Link Aggregation Group (LAG)
- Router Peer IPs / ASN
- Route Tables
- Colocation Facility / Partner Network
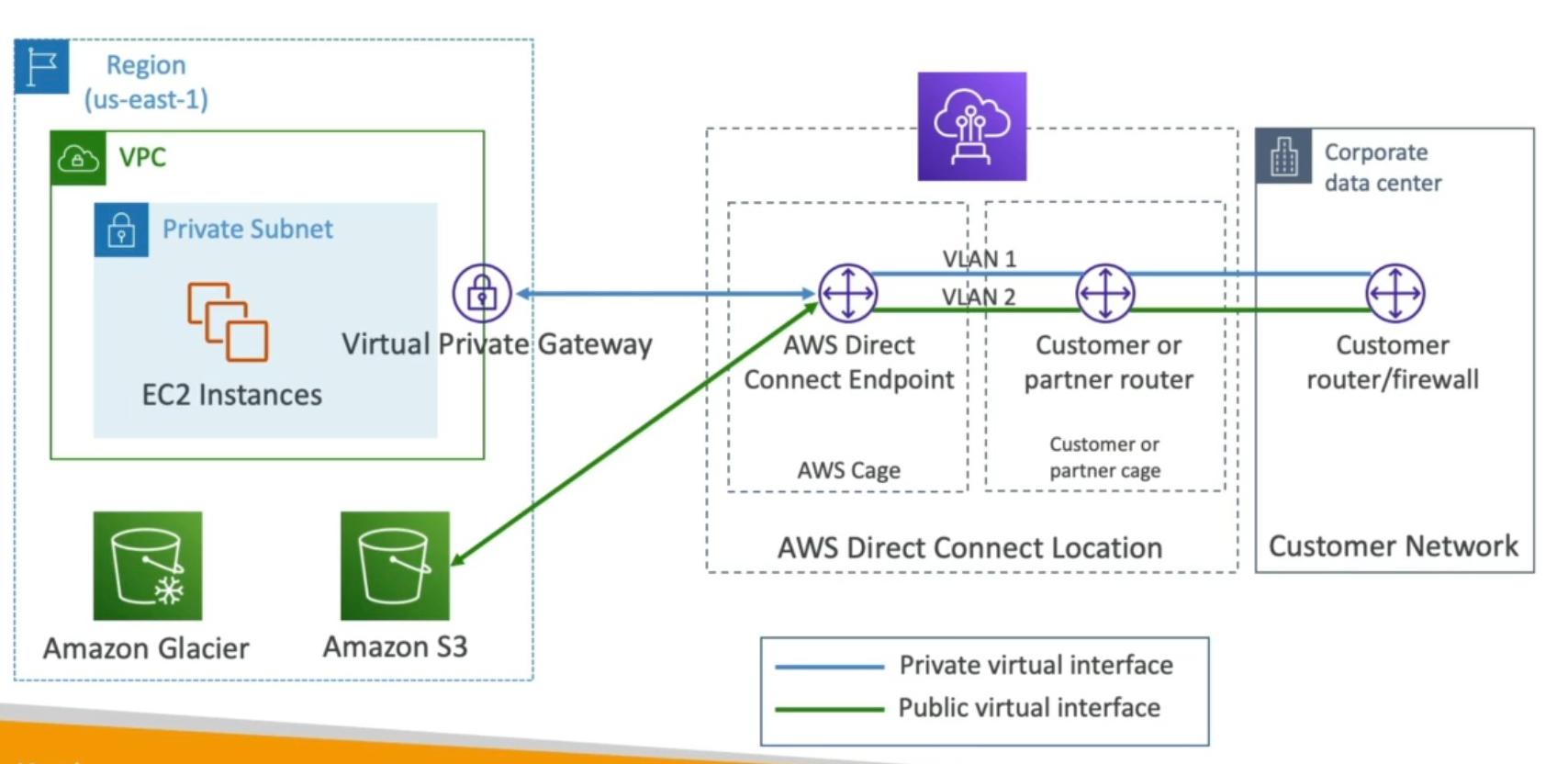 Dedicated private connection to remote network into VPC
Hybrid Model
VGW is used to setup the connction
Consistent network experience and increased bandwidth
Dedicated private connection to remote network into VPC
Hybrid Model
VGW is used to setup the connction
Consistent network experience and increased bandwidth
AWS Cage | Customer or partner cage for rent a router S2S as backup
- If theres’ an issue, you can setup S2S as backup for resiliency